Código
library(vcd)Una visualización de datos correcta puede expresar de forma resumida y clara gran cantidad de información, ayudando a interpretar y asimilar la información más facilmente.
library(vcd)mosaic(~ Class + Survived, data = Titanic, shade = TRUE, legend = TRUE)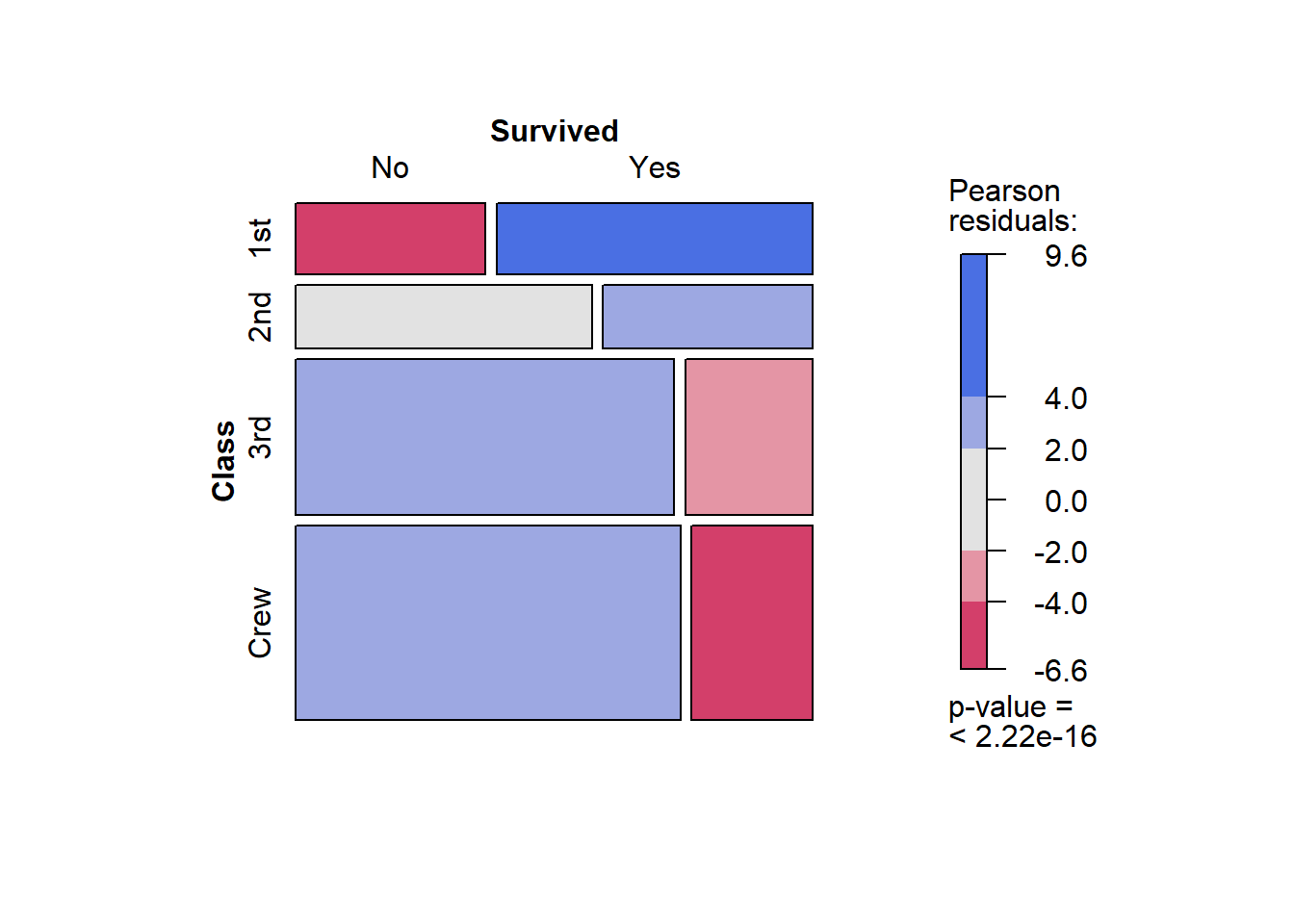
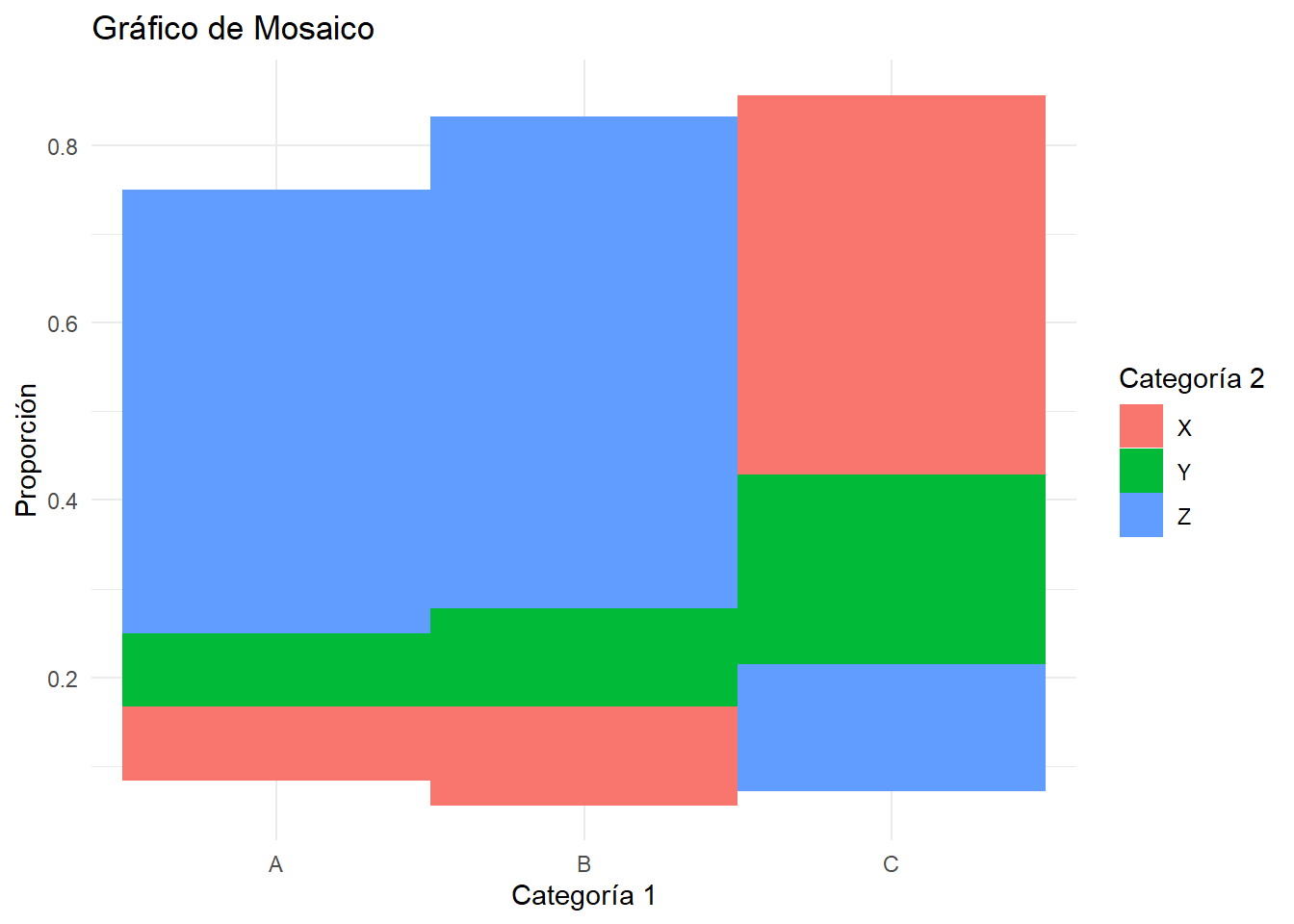
# Crear un marco de datos con categorías
data <- data.frame(
Categoria1 = rep(c("A", "B", "C"), each = 3),
Categoria2 = rep(c("X", "Y", "Z"), times = 3),
Count = c(10, 20, 30, 5, 15, 25, 20, 10, 5)
)
# Calcular proporciones
data <- data %>%
group_by(Categoria1) %>%
mutate(Proporcion = Count / sum(Count)) %>%
ungroup()
# Crear el gráfico de mosaico
ggplot(data, aes(x = Categoria1, y = Count, fill = Categoria2)) +
geom_tile(aes(height = Count)) +
labs(title = "Gráfico de Mosaico",
x = "Categoría 1",
y = "Proporción",
fill = "Categoría 2") +
theme_minimal()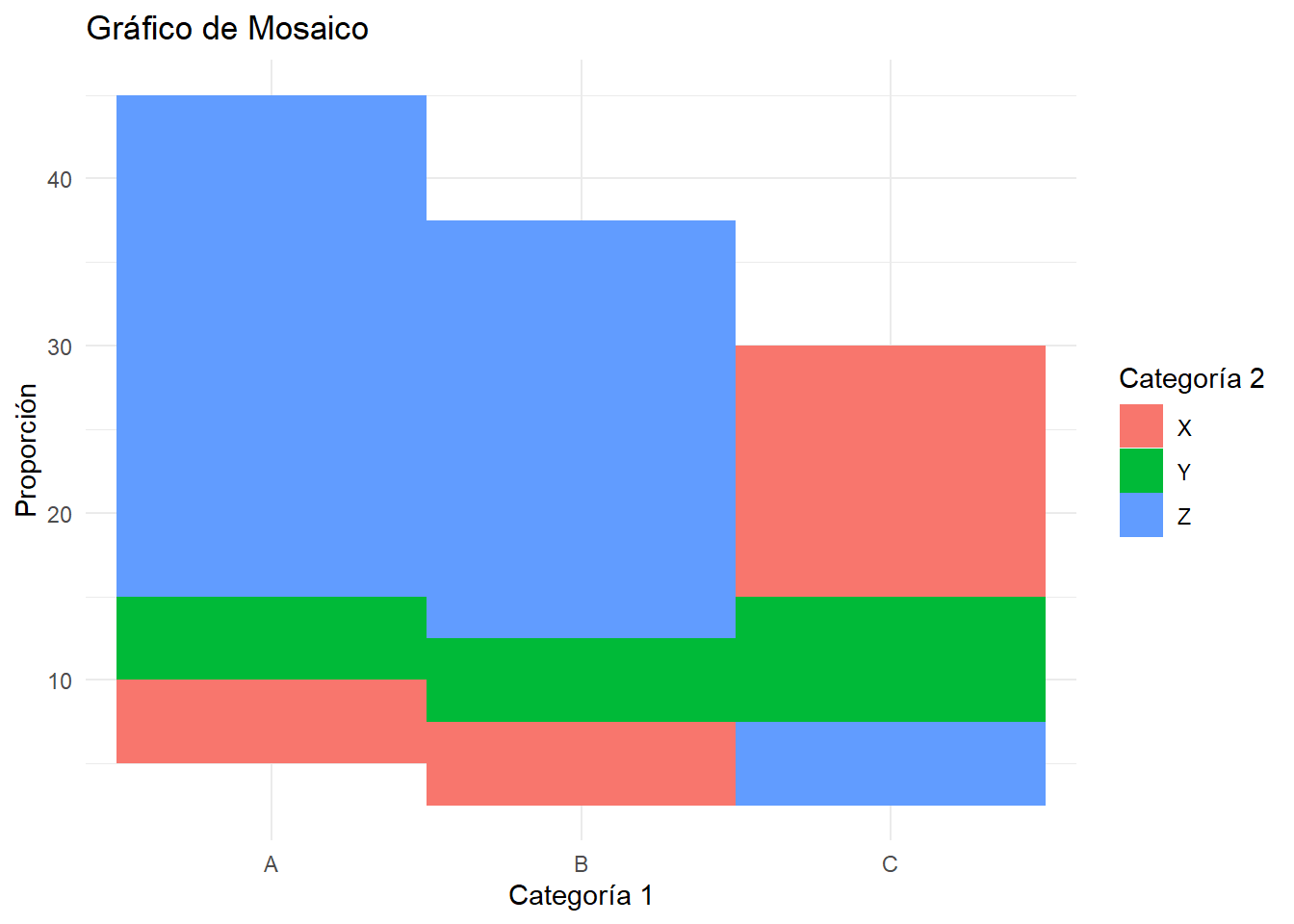
#ggplot(data = fly) +
# geom_mosaic(aes(x=product(do_you_recline), fill = do_you_recline,
# conds = product(rude_to_recline))) +
# labs(title='f(do_you_recline | rude_to_recline)')# Librerías
library(ggplot2)
library(treemapify)
# Datos
data <- data.frame(
category = c("A", "B", "C", "D"),
value = c(40, 30, 20, 10)
)
# Gráfico de árbol
ggplot(data, aes(area = value, fill = category, label = category)) +
geom_treemap() +
geom_treemap_text(colour = "white", place = "centre") +
labs(title = "Distribución de categorías")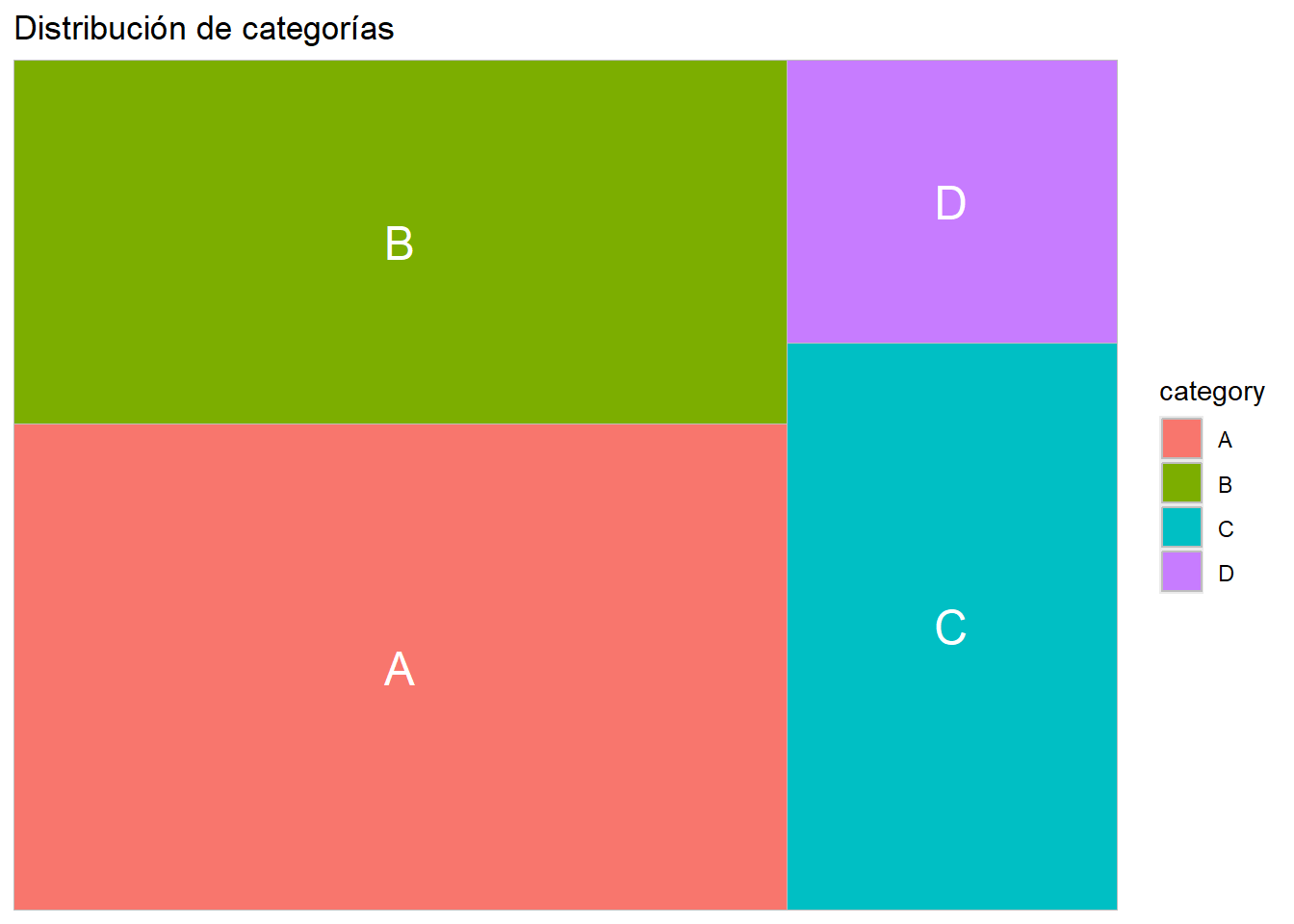
# Librerías
library(ggplot2)
library(maps)
# Datos
data <- map_data("state")
data$rate <- runif(nrow(data), min = 0, max = 1)
# Mapa coroplético
ggplot(data, aes(long, lat, group = group)) +
geom_polygon(aes(fill = rate), color = "white") +
scale_fill_continuous(low = "white", high = "blue") +
labs(title = "Tasa aleatoria por estado")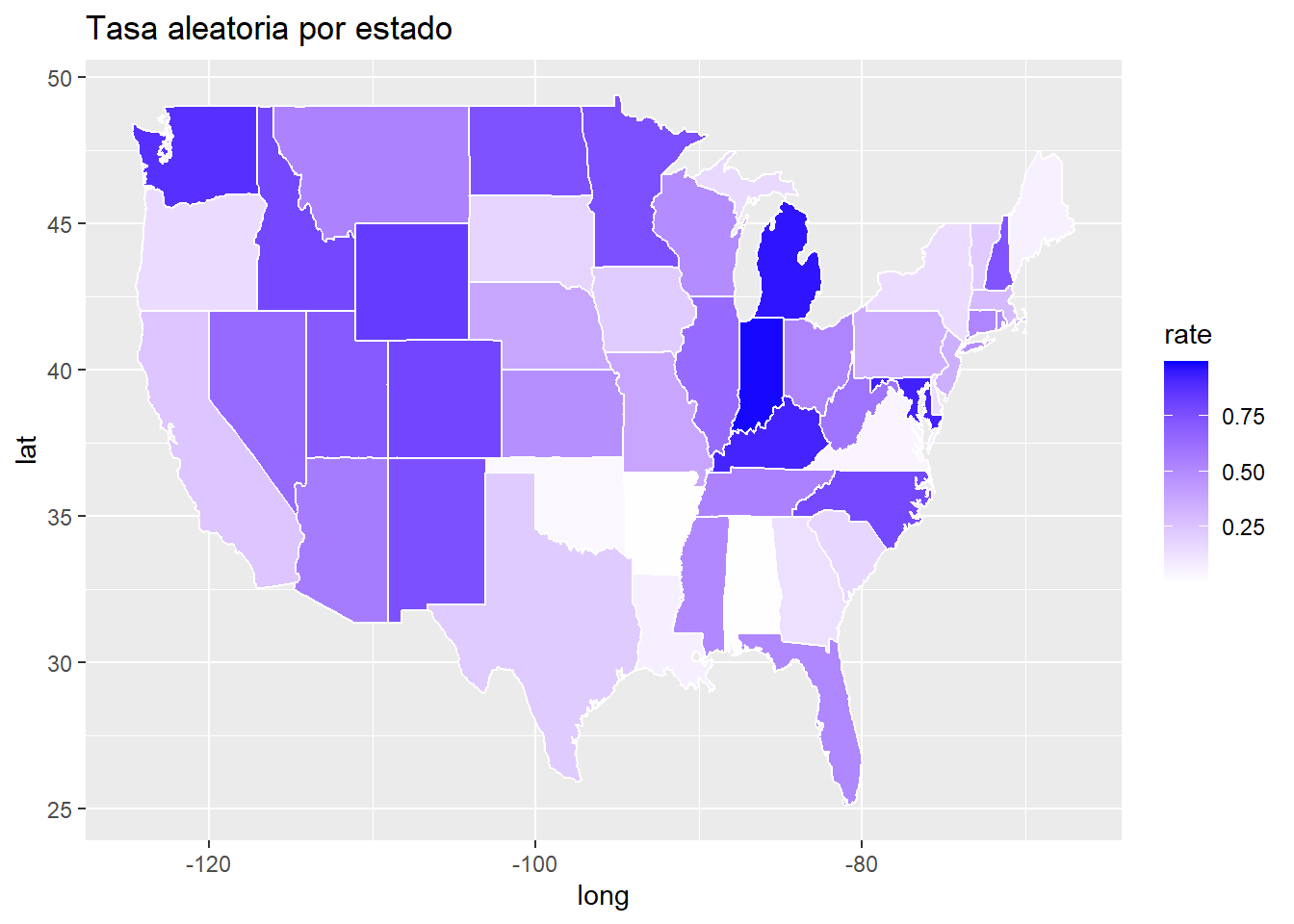
# Librerías
library(networkD3)
# Datos
nodes <- data.frame(name = c("A", "B", "C", "D"))
links <- data.frame(
source = c(0, 1, 1, 2, 3),
target = c(1, 2, 3, 3, 2),
value = c(10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
)
# Gráfico de Sankey
sankeyNetwork(Links = links, Nodes = nodes, Source = "source", Target = "target",
Value = "value", NodeID = "name", fontSize = 12)# Librerías
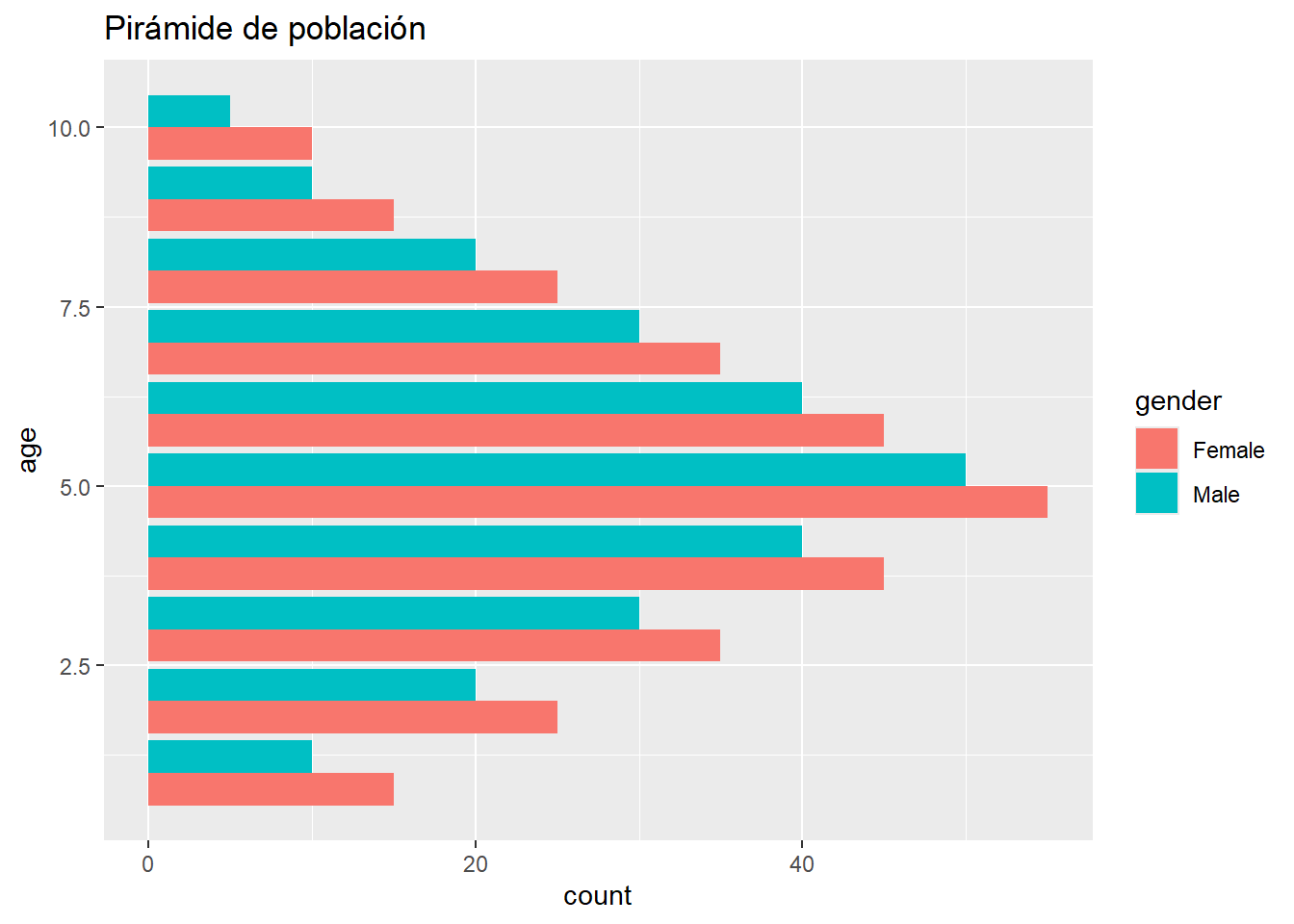
library(ggplot2)
# Datos
data <- data.frame(
age = rep(1:10, 2),
count = c(10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10, 5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 45, 35, 25, 15, 10),
gender = rep(c("Male", "Female"), each = 10)
)
# Gráfico de mariposa
ggplot(data, aes(x = age, y = count, fill = gender)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "dodge") +
coord_flip() +
labs(title = "Pirámide de población")
# Librerías
library(ggplot2)
# Datos
data <- data.frame(
x = rnorm(100),
y = rnorm(100),
size = rnorm(100, mean = 5, sd = 2)
)
# Gráfico de burbujas
ggplot(data, aes(x = x, y = y, size = size)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
labs(title = "Gráfico de burbujas")